Introduction
Planning for retirement might seem like a daunting task, especially when navigating the complexities of the investment world. But there’s a solution that can simplify retirement planning and potentially enhance returns: an ETF portfolio. ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, offer a bundle of stocks or bonds that trade on exchanges, providing diversification and cost-effectiveness. With a well-rounded ETF portfolio, you can potentially build a nest egg that will support your comfortable retirement. Here’s a deep dive into the ins and outs of creating an ETF portfolio specifically tailored for retirement.
Choosing the Right ETFs
Selecting the right ETFs is crucial for building an effective retirement portfolio. Start by assessing your risk tolerance, which gauges how much potential loss you’re comfortable with. This is largely influenced by your age, investment horizon, and financial situation. If you’re approaching retirement, a more conservative approach might be wise, while younger individuals may tolerate higher risk for potentially greater returns.
Consider your time horizon as well. How long do you plan to invest before tapping into your retirement funds? A shorter time horizon may call for a more conservative portfolio, while a longer one allows for a potentially more aggressive approach. Lastly, align your investment goals with your ETFs. If you’re aiming for growth, seek out ETFs that track growth-oriented indices. If income is a priority, consider ETFs focused on dividend-paying stocks or bonds.
Types of ETFs for Retirement
The world of ETFs offers a wide range of options, including:
1. Target-date funds: These funds are designed to automatically adjust their asset allocation as you approach retirement. As you get closer to retirement, the fund gradually shifts from stocks to bonds, reducing risk.
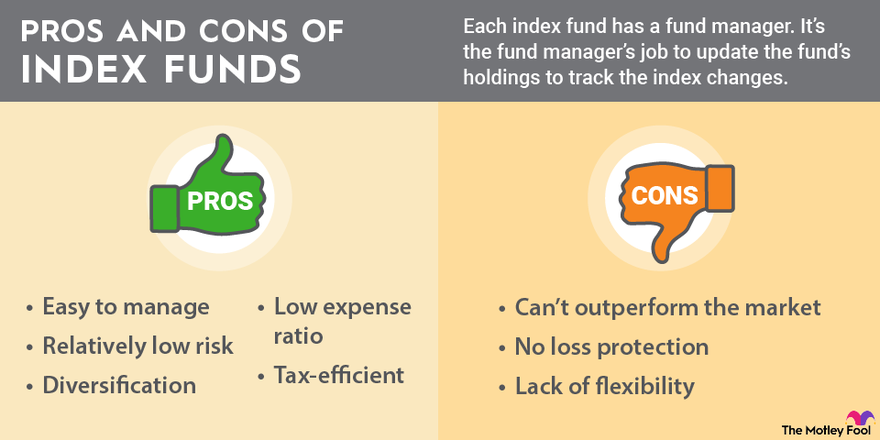
2. Index funds: These track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or the total bond market. They provide broad diversification at a low cost.
3. Sector or industry ETFs: These focus on specific sectors or industries, offering more targeted exposure. For example, you could invest in an ETF that tracks the technology sector or the healthcare industry.
Building a Retirement ETF Portfolio
For those nearing retirement, securing a comfortable financial future is paramount. One effective means of achieving this is by crafting a well-diversified ETF portfolio. ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, offer investors a convenient and cost-efficient way to access a broad spectrum of assets. By carefully selecting ETFs that align with their risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment goals, individuals can optimize their retirement savings.
Determining Your Key Considerations
-
Risk Tolerance: Every investor has a unique appetite for risk. Some prefer to prioritize safety and stability, while others are willing to embrace higher levels of volatility in pursuit of greater potential returns. Assessing your risk tolerance is crucial to determining the appropriate mix of ETFs in your portfolio.
-
Time Horizon: The length of time until your planned retirement date is a significant factor. Those with a shorter time horizon may opt for a more conservative portfolio, emphasizing bonds over stocks. Conversely, those with a longer time horizon can potentially afford to assume more risk by investing a larger portion in stocks.
-
Investment Goals: Clearly define your retirement income needs and goals. This step helps guide your ETF selection by ensuring that your portfolio is tailored to meet your specific objectives. Consider factors such as your desired retirement lifestyle, healthcare expenses, and any other anticipated financial obligations.
Building Your ETF Portfolio
Based on the above considerations, here’s how to build a well-rounded retirement ETF portfolio:
-
Start with a Core Holding: Begin with a broad-market ETF that tracks a major index like the S&P 500. This provides instant diversification and captures the overall performance of the stock market.
-
Add International Exposure: Diversify further by allocating a portion of your portfolio to international ETFs. These investments provide exposure to different economies and potentially mitigate the risks associated with investing solely in domestic companies.
-
Include Fixed Income: Bonds play a vital role in reducing portfolio volatility and providing a steady stream of income. Consider adding bond ETFs with varying maturities to enhance portfolio stability.
-
Consider Sector Rotation: To potentially enhance returns, allocate a small portion of your portfolio to sector-specific ETFs. These ETFs provide exposure to specific industries, such as healthcare or technology, allowing you to capitalize on potential growth opportunities.
-
Monitor and Rebalance Regularly: As your circumstances and market conditions change, it’s essential to monitor your portfolio and make adjustments as needed. Rebalancing involves periodically selling some ETFs and buying others to maintain your desired asset allocation and risk level.
By following these steps, you can construct a robust retirement ETF portfolio that aligns with your individual needs and goals. Remember, the key is to strike a balance between risk and return, ensuring that your investments are positioned to help you achieve a financially secure retirement.
The Best ETF Portfolio for Retirement: A Guide to Choosing and Managing Your Investments
Securing a comfortable retirement requires thoughtful financial planning, and investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) can be a savvy move. ETFs offer a diversified, cost-effective way to gain exposure to various markets, making them an ideal choice for long-term investors.
Selecting the Optimal ETFs
Choosing the right ETFs is crucial for achieving your retirement goals. Start by determining your risk tolerance and time horizon. If you’re years away from retirement, you may opt for growth-oriented ETFs that track the performance of the S&P 500 or other broad market indices. As you approach retirement age, consider allocating a portion of your portfolio to income-generating ETFs, such as those focused on bonds or real estate investment trusts (REITs).
A Sample ETF Portfolio
Here’s a sample ETF portfolio for retirement:
- Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI): Tracks the entire U.S. stock market, providing broad diversification.
- Vanguard Total International Stock ETF (VXUS): Provides exposure to international markets, reducing overall risk.
- Vanguard Total Bond Market ETF (BND): Tracks the U.S. bond market, offering stability and income.
- Vanguard Real Estate ETF (VNQ): Invests in REITs, providing exposure to the real estate market and potential income.
Rebalancing and Monitoring
Rebalance Regularly
Over time, your investments may drift from your desired asset allocation as some ETFs outperform others. Rebalancing involves adjusting your portfolio to maintain your target allocation. For instance, if your stock ETFs have performed well and now make up 70% of your portfolio, you might sell some stock ETFs and purchase bond ETFs to bring your allocation back to 60% stocks and 40% bonds.
Monitor Performance
Keep track of your ETFs’ performance by monitoring their returns, expense ratios, and other relevant metrics. If an ETF consistently underperforms or incurs high expenses, consider replacing it with a better option. Regular monitoring allows you to make informed decisions and adjust your portfolio as needed.
Seek Professional Advice
Consider consulting a financial advisor to optimize your retirement ETF portfolio. They can assess your individual circumstances, provide personalized recommendations, and guide you through the investment process. Professional advice can help you avoid costly mistakes and maximize your retirement savings.
No responses yet