How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing industries from finance to supply chain management. But how does it actually work? It can be a bit like putting together a giant jigsaw puzzle, where each piece is a verified transaction. These transactions are bundled up into blocks, which are then added to the blockchain, creating a permanent record that’s virtually unchangeable.
Block Creation
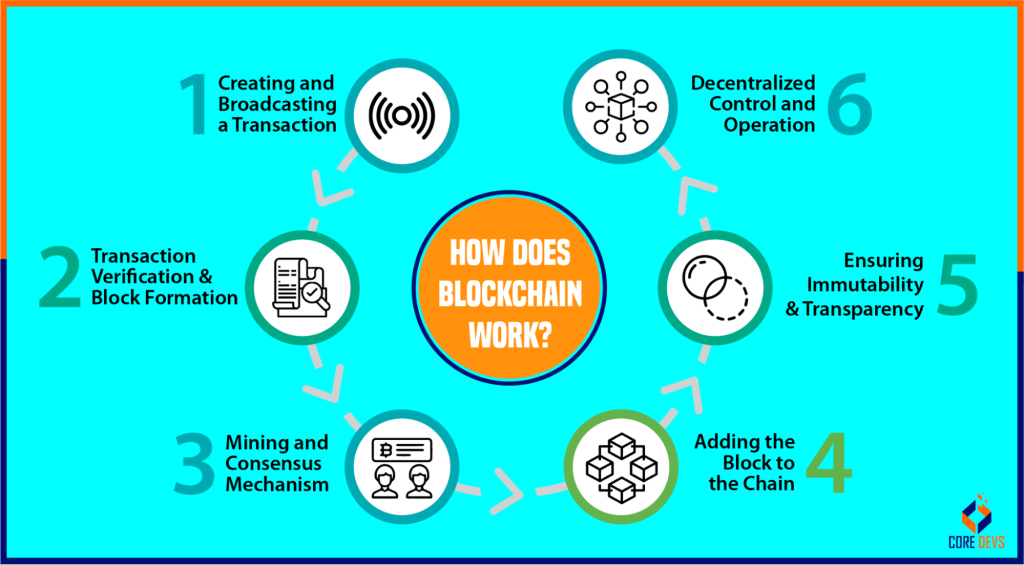
Imagine you’re managing a busy town square where people are constantly making transactions. To keep track of everything, you decide to group these transactions into blocks, like each day’s receipts. Each block contains a certain number of transactions, along with a unique code called a hash. This hash is like a fingerprint that helps identify the block and ensures its integrity.
Once a block is filled up, it’s ready to be added to the blockchain. But before it can join the chain, it needs to be verified by multiple computers, known as nodes. Nodes are like independent auditors who check to make sure the transactions in the block are legitimate and haven’t been tampered with.
Verification and Validation
Verifying transactions is like sorting through a pile of invoices to make sure they’re all valid. Nodes check the authenticity of each transaction by ensuring that the sender has the funds to make the payment and that the recipient’s account is valid. If everything checks out, the transaction is considered valid.
Once a block’s transactions are verified, they’re ready to be validated. Validation involves adding the block to the blockchain and broadcasting it to all the other nodes on the network. Each node then independently verifies the block and adds it to its own copy of the blockchain. This creates a decentralized and tamper-proof record of all the transactions that have ever taken place on the blockchain.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Blockchain technology is the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. But how does it work? In essence, a blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
When a new transaction occurs, it is broadcast to the network of computers that maintain the blockchain. These computers, called nodes, verify the transaction and add it to a new block. The new block is then broadcast to the network and added to the blockchain, becoming a permanent part of the ledger.
This process ensures that transactions are secure, immutable, and transparent. Blockchain technology is decentralized, meaning that it is not controlled by any single entity. Instead, the network is maintained by a vast number of nodes, making it resistant to hacking and censorship.
Challenges
Despite its benefits, blockchain technology faces challenges in scalability and regulation. Scalability refers to the ability of a blockchain to handle a large number of transactions. As the number of users and transactions increases, the blockchain can become slow and expensive to use.
Regulation is another challenge for blockchain technology. Governments around the world are still struggling to develop a clear regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies and other blockchain-based applications. This uncertainty can make it difficult for businesses to adopt blockchain technology.
Benefits
Despite these challenges, blockchain technology offers several potential benefits. It can increase transparency, reduce costs, and improve security. Blockchain technology can also be used to create new and innovative applications, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a powerful tool with the potential to revolutionize many industries. However, it faces challenges in scalability and regulation. As these challenges are overcome, blockchain technology is likely to become even more widely adopted.
No responses yet