What is Blockchain Technology?
What is blockchain technology? If you’re scratching your head, don’t worry – you’re not alone. Blockchain is one of those buzzwords that seems to be everywhere these days, but it can be tough to understand. Simply put, blockchain is a digital ledger – a special kind of database – that keeps a secure, unforgeable record of transactions. Think of it as a giant, shared spreadsheet that’s constantly being updated and verified by a network of computers.
The beauty of blockchain is that it’s decentralized. That means it’s not controlled by any single entity, like a bank or a government. Instead, it’s maintained by a network of computers spread all over the world. This makes it extremely secure because there’s no central point of failure. If one computer goes down, the rest of the network can still keep going.
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize many different industries, not just finance. It can be used to create more efficient and transparent supply chains, improve healthcare data management, and even create new forms of digital currency. As more and more people start to understand blockchain, we’re sure to see even more innovative uses for this groundbreaking technology.
What is Blockchain Technology?
If you’re wondering, "What is blockchain technology?" then you’re in the right place. Blockchain technology is a revolutionary concept that has the potential to transform many industries. In essence, it’s a decentralized, secure way of recording and managing data. Let’s delve into the specifics and explore the intriguing world of blockchain.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
-
Decentralization:
Blockchain’s decentralized nature is its defining feature. Unlike traditional systems where data is stored in a central location, blockchain distributes it across a network of computers. This eliminates single points of failure and makes it incredibly difficult to hack or manipulate the data. It’s like a group of friends keeping a ledger, rather than trusting all the information to just one person. -
Security:
Blockchain technology is ultra-secure, employing cryptography and advanced algorithms to protect data. It’s like putting an unbreakable lock on a fort full of precious treasures. Each block of data is encrypted and linked to the previous block, creating a chain. If a hacker tries to change one block, the entire chain would be affected, raising a red flag and alerting everyone. -
Transparency:
Transparency is the backbone of blockchain technology. Transactions and data are recorded on a public ledger that everyone can view. It’s like a financial report that’s open to the public, leaving no room for hidden dealings. This transparency fosters trust and accountability, as everyone has access to the same information. -
Immutability:
Once data is entered into a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. It’s like writing on a stone tablet—once it’s there, it’s there forever. This makes blockchain an ideal way to record transactions, contracts, and other important documents, ensuring their authenticity and validity over time.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
In an era where digitization reigns supreme, blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing the way we interact with digital information. At its core, blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. This innovative approach ensures the transparency, integrity, and security of data, paving the way for a myriad of groundbreaking applications across various industries.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology in Finance
The finance industry has particularly embraced the transformative potential of blockchain technology. By leveraging its unique capabilities, financial institutions can unlock a wealth of benefits, including:
-
Enhanced Efficiency: By eliminating the need for intermediaries and automating processes, blockchain dramatically streamlines financial transactions. This not only reduces the time required to execute transactions but also eliminates errors often associated with manual processing.
-
Reduced Costs: The elimination of intermediaries and the automation of processes lead to significant cost savings for financial institutions. These savings can be passed on to consumers in the form of lower fees and more competitive interest rates.
-
Increased Transparency: Blockchain technology ensures that all transactions are recorded on a public ledger, providing complete visibility and accountability. This level of transparency fosters trust among participants and reduces the risk of fraud and financial malfeasance.
-
Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithms make it virtually impenetrable to unauthorized access or data manipulation. Each transaction is linked to the previous one, creating an unbreakable chain of evidence that ensures the integrity of financial records.
-
New Financial Products and Services: Blockchain’s innovative capabilities have spurred the development of new financial products and services. These include decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, which enable peer-to-peer lending, trading, and other financial services without the need for traditional financial institutions.
What is Blockchain Technology: A Journey into the Future of Digital Transactions
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the world of digital transactions, promising to transform industries and reshape the way we do business. But what is blockchain technology, and why does it matter?
Blockchain, in simple terms, is a shared, secure, and immutable digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each block in the chain contains a set of transactions, and once added, it becomes a permanent part of the ledger. This secure and auditable system eliminates the need for intermediaries and makes it virtually impossible to tamper with data.
Challenges and Future of Blockchain Technology
While blockchain has immense potential, it also faces challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption. These include:
1. Scalability: Blockchain networks can face performance limitations when handling large volumes of transactions.
2. Interoperability: Different blockchain platforms may have their own unique protocols and standards, making it difficult to exchange data and assets across them.
3. Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and regulatory bodies are still in the process of developing clear and consistent frameworks for blockchain technology.
4. Security: While blockchain is highly secure, vulnerabilities can arise from smart contract bugs or external attacks.
5. Privacy: Public blockchains provide transparency but may not meet the privacy requirements of certain applications. Zero-knowledge proofs and other privacy-enhancing techniques are being explored to address this.
6. Standards and Adoption: The lack of standardization and widespread adoption can hinder the growth and maturity of blockchain technology.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain technology looks bright. As scalability is improved, interoperability is addressed, and regulatory frameworks become more robust, blockchain is poised to revolutionize a wide range of industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and even voting systems. By enhancing security, automating processes, and reducing costs, blockchain has the potential to make our digital world more efficient, secure, and transparent.
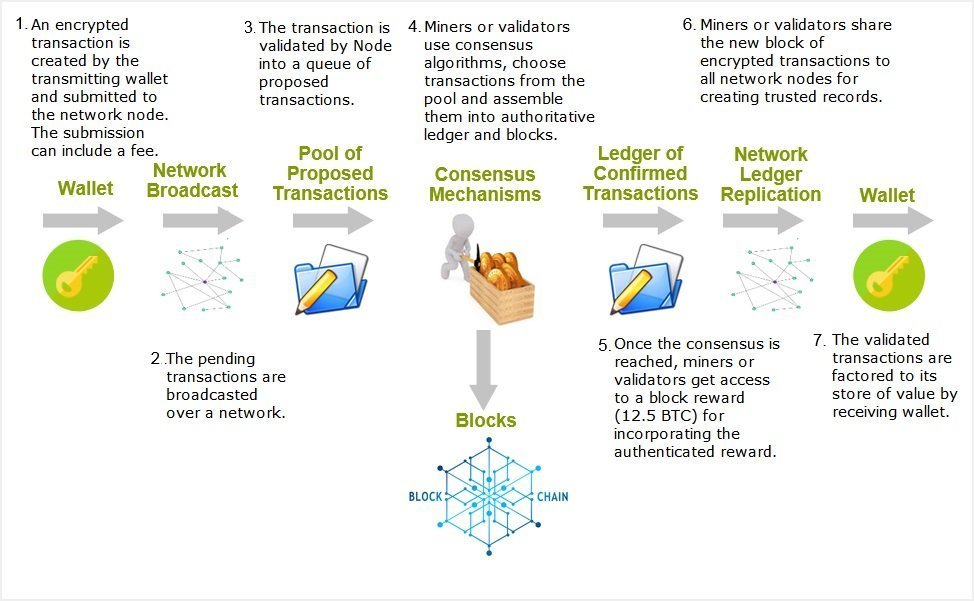
No responses yet